简介 :Shiro讲解,涉及身份认证/登录,验证用户是不是拥有相应的身份;授权,及权限验证;会话管理,用户登录后就一次会话;加密,保护数据安全
初步认识
- 一个安全认证,授权框架
- 轻量级的(从jar,从设计)
- 现成的组件
模块简介

模块说明
- Authentication : 身份认证/登录,验证用户是不是拥有相应的身份
- Authorization :授权,及权限验证
- Session Manager : 会话管理,用户登录后就一次会话
- Cryptography :加密,保护数据安全
- Web Support: web支持,可以非常容易的集成到web
- Caching : 缓存
- Concurrency: shiro支持多线程应用
- Testing:测试
- Run As :允许一个用户假装为另一个用户
- Remember me:记住我
Shiro 不会去维护用户,维护权限;需要我们自己去设计,然后注入Shiro
优点
- 简洁的API,使用方便灵活
- 可插拔式,能与其他很多框架完美融合
- web能力,remenber me,以及缓存的设计
- 不依赖于具体环境,无论是web,application
式例
- maven
1
2
3
4
5
6<!-- 引入依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.2</version>
</dependency>
其日志是面向slf4j 编程的,所以如果要友好的显示日志,可以根据自己的习惯导入(log4j,logback ….)
shiro.ini
1
2
3[users]
pxw=123
jjb=123code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13// 创建SecurityManager
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
// 对SecurityUtils 设置SecurityManager
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// 创建Token
AuthenticationToken aToken = new UsernamePasswordToken("pxw", "123");
// 获取Subject目标
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 登录
subject.login(aToken);
boolean auth = subject.isAuthenticated();
System.out.println("是否已经登录:" + auth);
身份认证 - Authentication
流程图
主要通过 Subject.login(token) 来进行身份认证
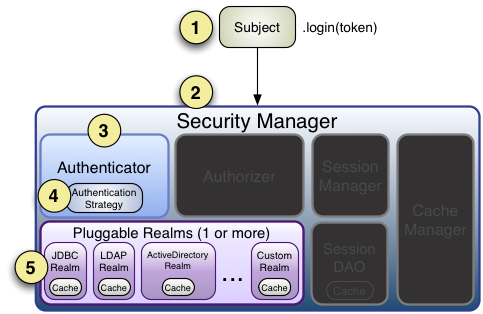
流程分析
- 首先调用Subject.login(token)进行登录,其会自动委托给Security Manager,调用之前必
须通过SecurityUtils. setSecurityManager()设置; - SecurityManager负责真正的身份验证逻辑;它会委托给Authenticator进行身份验证;
- Authenticator才是真正的身份验证者,Shiro API中核心的身份认证入口点,此处可以自
定义插入自己的实现; - Authenticator可能会委托给相应的AuthenticationStrategy进行多Realm身份验证,默认
ModularRealmAuthenticator会调用AuthenticationStrategy进行多Realm身份验证; - Authenticator 会把相应的token 传入Realm,从Realm 获取身份验证信息,如果没有返
回/抛出异常表示身份验证失败了。此处可以配置多个Realm,将按照相应的顺序及策略进
行访问。
上述说明可能会造成理解的不畅,注意这几个要点
1 | ## 接口SecurityManager 是继承 Authenticator |
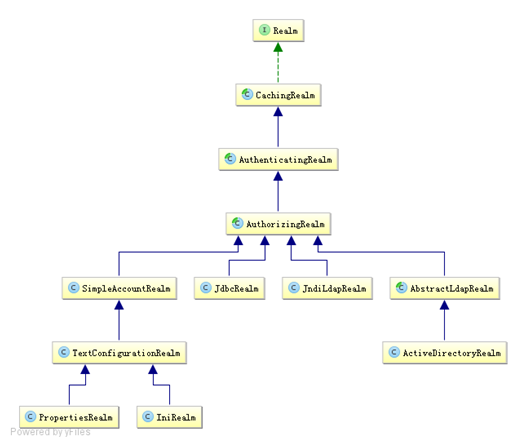
Realm 的实现体系
Realm:域,Shiro从从Realm获取安全数据(如用户、角色、权限),就是说SecurityManager要验证用户身份,那么它需要从Realm获取相应的用户进行比较以确定用户身份是否合法;也需要从Realm得到用户相应的角色/权限进行验证用户是否能进行操作;可以把Realm看成DataSource,即安全数据源。如我们之前的ini配置方式将使用org.apache.shiro.realm.text.IniRealm。
如果身份验证失败请捕获AuthenticationException 或其子类,常见的如:
- DisabledAccountException(禁用的帐号)
- LockedAccountException(锁定的帐号)
- UnknownAccountException(错误的帐号)
- ExcessiveAttemptsException(登录失败次数过多)
- IncorrectCredentialsException (错误的凭证)
- ExpiredCredentialsException(过期的凭证)等,
具体请查看其继承关系;对于页面的错误消息展示,最好使用如“用户名/密码错误”
而不是“用户名错误”/“密码错误”,防止一些恶意用户非法扫描帐号库
多个Realm
1 | # |
securityManager.realms 可不指定,默认会依次读取,如果显示指定,按指定顺序读取
多Realm的验证策略 AuthenticationStrategy
SecurityManager接口继承了Authenticator,另外还有一个ModularRealmAuthenticator实现,
其委托给多个Realm 进行验证,验证规则通过AuthenticationStrategy 接口指定,
- FirstSuccessfulStrategy:只要有一个Realm验证成功即可,只返回第一个Realm身份验证
成功的认证信息,其他的忽略; - AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy:只要有一个Realm验证成功即可,和FirstSuccessfulStrategy
不同,返回所有Realm身份验证成功的认证信息; - AllSuccessfulStrategy:所有Realm验证成功才算成功,且返回所有Realm身份验证成功的
认证信息,如果有一个失败就失败了。 - ModularRealmAuthenticator默认使用AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy策略。
shiro.ini1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13[main]
#指定securityManager的authenticator实现
authenticator=org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator
securityManager.authenticator=$authenticator
#指定securityManager.authenticator的authenticationStrategy
allSuccessfulStrategy=org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AllSuccessfulStrategy
securityManager.authenticator.authenticationStrategy=$allSuccessfulStrategy
myRealm1=com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.realm.MyRealm1
myRealm2=com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.realm.MyRealm2
myRealm3=com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.realm.MyRealm3
securityManager.realms=$myRealm1,$myRealm3
自定义策略 略
授权 - Authorization
概念
- 主体(Subject)
- 资源(Resource)
- 权限(permission)
- 角色(Role)
基于角色的权限访问控制RBAC(role-based access control)是以角色为中心进行的访问控制,也就是判断主体subject是那个角色的方式进行权限访问控制,是粗粒度的 (隐式角色)
基于资源的权限访问控制RBAC(resource-based access control)是以资源为中心进行的访问控制,只需要为角色添加权限就可以 (显示角色)
授权方式
编程式 :通过写if/else 授权代码块完成
1
2
3
4
5
6Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if(subject.hasRole(“admin”)) {
//有权限
} else {
//无权限
}注解式:通过在执行的Java方法上放置相应的注解完成
1
2
3
4@RequiresRoles("admin")
public void hello() {
//有权限
}JSP/GSP 标签:在JSP/GSP 页面通过相应的标签完成
1
2
3<shiro:hasRole name="admin">
<!— 有权限—>
</shiro:hasRole>
授权
ini配置规则 “用户名=密码,角色1,角色2” “角色=权限1,权限2”
1 | #示例 shiro-rbac.ini |
Shiro 提供的checkRole/checkRoles 和hasRole/hasAllRoles 不同的地方是它在判断为假的情
况下会抛出UnauthorizedException异常。
Shiro 提供了isPermitted 和isPermittedAll 用于判断用户是否拥有某个权限或所有权限,也
没有提供如isPermittedAny用于判断拥有某一个权限的接口
Permission
规则:“资源标识符:操作:对象实例ID” 即对哪个资源的哪个实例可以进行什么操作。
其默认支持通配符权限字符串,“:”表示资源/操作/实例的分割;“,”表示操作的分割;
“*”表示任意资源/操作/实例
1 | role41=system:user:update,system:user:delete |
多个冒号就需要 多个*来匹配
性能问题:
通配符匹配方式比字符串相等匹配来说是更复杂的,因此需要花费更长时间,但是一般系统的权限不会太多,且可以配合缓存来提供其性能,如果这样性能还达不到要求我们可以实现位操作算法实现性能更好的权限匹配。另外实例级别的权限验证如果数据量太大也不建议使用,可能造成查询权限及匹配变慢。可以考虑比如在sql 查询时加上权限字符串之类的方式在查询时就完成了权限匹配。
授权流程
- 首先调用Subject.isPermitted/hasRole接口,其会委托给SecurityManager,而
SecurityManager接着会委托给Authorizer; - Authorizer是真正的授权者,如果我们调用如isPermitted(“user:view”),其首先会通过
PermissionResolver把字符串转换成相应的Permission实例; - 在进行授权之前,其会调用相应的Realm获取Subject相应的角色/权限用于匹配传入的
角色/权限; - Authorizer会判断Realm的角色/权限是否和传入的匹配,如果有多个Realm,会委托给
ModularRealmAuthorizer 进行循环判断,如果匹配如isPermitted/hasRole会返回true,否
则返回false表示授权失败。
ModularRealmAuthorizer进行多Realm匹配流程:
- 首先检查相应的Realm是否实现了实现了Authorizer;
- 如果实现了Authorizer,那么接着调用其相应的isPermitted/hasRole接口进行匹配;
- 如果有一个Realm匹配那么将返回true,否则返回false。如果Realm进行授权的话,应该继承AuthorizingRealm
其流程是:
- 如果调用hasRole*,则直接获取AuthorizationInfo.getRoles()与传入的角色比较即可;
- 首先如果调用如isPermitted(“user:view”),首先通过PermissionResolver 将权限字符串
转换成相应的Permission 实例,默认使用WildcardPermissionResolver,即转换为通配符的
WildcardPermission; - 通过AuthorizationInfo.getObjectPermissions() 得到Permission 实例集合;通过
AuthorizationInfo. getStringPermissions()得到字符串集合并通过PermissionResolver 解析为
Permission 实例;然后获取用户的角色,并通过RolePermissionResolver 解析角色对应的权
限集合(默认没有实现,可以自己提供); - 接着调用Permission. implies(Permission p)逐个与传入的权限比较,如果有匹配的则返回
true,否则false。
ini 详解
1 | [main] |
加解密 - Cryptography
编码/解码
- Shiro 提供了base64和16进制字符串编码/解码的API支持
1 | String str = "hello"; |
1 | String str = "hello"; |
CodecSupport,提供了toBytes(str, “utf-8”) / toString(bytes,
“utf-8”)用于在byte 数组/String 之间转换。
散列算法
- 散列算法一般用于生成数据的摘要信息,是一种不可逆的算法,一般适合存储密码之类的
数据,常见的散列算法如MD5、SHA等 - 为了方便使用,Shiro 提供了HashService,默认提供了DefaultHashService实现。
1 | DefaultHashService hashService = new DefaultHashService(); //默认算法SHA-512 |
加密/解密
- Shiro 还提供对称式加密/解密算法的支持,如AES、Blowfish 等;当前还没有提供对非对
称加密/解密算法支持,
1 | AesCipherService aesCipherService = new AesCipherService(); |
PasswordService/CredentialsMatcher
- Shiro 提供了PasswordService及CredentialsMatcher用于提供加密密码及验证密码服务。
密码重试次数限制
会话管理
Shiro 提供了完整的企业级会话管理功能,不依赖于底层容器(如web容器tomcat),不管
JavaSE 还是JavaEE环境都可以使用,提供了会话管理、会话事件监听、会话存储/持久化、
容器无关的集群、失效/过期支持、对Web 的透明支持、SSO 单点登录的支持等特性。即
直接使用Shiro 的会话管理可以直接替换如Web 容器的会话管理。
会话
1 | Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); |
包含方法
1 | #id 会话的唯一标识 |
Shiro 提供的会话可以用于JavaSE/JavaEE 环境,不依赖于任何底层容器,可以独立使用,
是完整的会话模块。
会话管理器
会话管理器管理着应用中所有Subject的会话的创建、维护、删除、失效、验证等工作。是Shiro 的核心组件。
顶层组件SecurityManager 直接继承了SessionManager,且提供了SessionsSecurityManager 实现直接把会话管理委托给相应的SessionManager ,DefaultSecurityManager 及DefaultWebSecurityManager 默认SecurityManager 都继承了
SessionsSecurityManager。
SecurityManager提供了如下接口:
1 | Session start(SessionContext context); //启动会话 |

Shiro提供了三个默认实现:
- DefaultSessionManager:DefaultSecurityManager使用的默认实现,用于JavaSE环境;
- ServletContainerSessionManager:DefaultWebSecurityManager使用的默认实现,用于Web环境,其直接使用Servlet容器的会话;
- DefaultWebSessionManager:用于Web环境的实现,可以替代ServletContainerSessionManager,自己维护着会话,直接废弃了Servlet容器的会话管理。
会话监听
会话监听器用于监听会话创建、过期及停止事件:
如果只想监听某一个事件,可以继承SessionListenerAdapter实现:
会话存储/持久化
Shiro 提供SessionDAO 用于会话的CRUD,即DAO(Data Access Object)模式实现:
Shiro内嵌了如下SessionDAO实现

AbstractSessionDAO提供了SessionDAO的基础实现,如生成会话ID等;CachingSessionDAO
提供了对开发者透明的会话缓存的功能,只需要设置相应的CacheManager 即可;
MemorySessionDAO 直接在内存中进行会话维护;而EnterpriseCacheSessionDAO 提供了缓
存功能的会话维护,默认情况下使用MapCache 实现,内部使用ConcurrentHashMap 保存
缓存的会话。
Shiro 提供了使用Ehcache 进行会话存储,Ehcache 可以配合TerraCotta 实现容器无关的分
布式集群。
会话验证
Shiro 提供了会话验证调度器,用于定期的验证会话是否已过期,如果过期将停止会话;出于性能考虑,一般情况下都是获取会话时来验证会话是否过期并停止会话的;但是如在web环境中,如果用户不主动退出是不知道会话是否过期的,因此需要定期的检测会话是否过期,Shiro提供了会话验证调度器SessionValidationScheduler来做这件事情。
sessionFactory
sessionFactory 是创建会话的工厂,根据相应的Subject上下文信息来创建会话;默认提供了SimpleSessionFactory用来创建SimpleSession会话。
其他模块
JSP标签
Shiro 提供了JSTL标签用于在JSP/GSP 页面进行权限控制,如根据登录用户显示相应的页面按钮。
首先 先在页面导入taglib
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
<zhang:hasAllRoles name="admin,user">
用户[<shiro:principal/>]拥有角色admin 和user<br/>
</zhang:hasAllRoles>
<zhang:hasAllPermissions name="user:create,user:update">
用户[<shiro:principal/>]拥有权限user:create和user:update<br/>
</zhang:hasAllPermissions>
<zhang:hasAnyPermissions name="user:create,abc:update">
用户[<shiro:principal/>]拥有权限user:create或abc:update<br/>
</zhang:hasAnyPermissions>
缓存机制
Shiro 提供了类似于Spring的Cache抽象,即Shiro本身不实现Cache,但是对Cache 进行了又抽象,方便更换不同的底层Cache实现。
Shiro提供的Cache接口:
1 | public interface Cache<K, V> { |
SSL
对于SSL的支持,Shiro 只是判断当前url是否需要SSL登录,如果需要自动重定向到https
进行访问。
1 | <filter> |
注: 该filter 会依赖于WebApplicationContext ,如果在springmvc中,不启动WebApplicationContext,直接从server 启动 Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet ‘spring’,那么如果有上面这个filter,则在容器请求时,会报错
java.lang.IllegalStateException: No WebApplicationContext found: no ContextLoaderListener registered?